While traveling you may often experience buzzing in your ears or being unable to hear well after the plane takes off or you go into a tunnel. There are many reasons for this and since it’s a common occurence we’ll talk about the Ear first. It is not rare that sometimes this is the case of hearing aids.
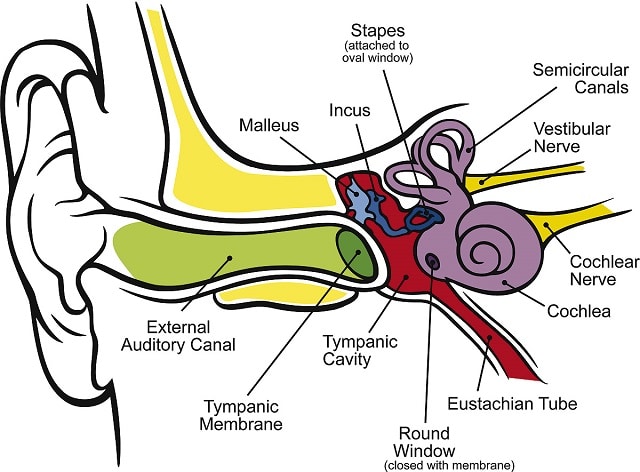
The ear is equipped with various components that are capable of picking up the external auditory stimulus (sound waves) and turn it into a nervous impulse intensity of a sound that is related to the amount of sound energy that crosses perpendicularly the surface per unit time. The cone shape of the ear allows it to pick up the sounds and direct them to the eardrum which starts to vibrate and these vibrations are transferred to scroll through three tiny bones that amplify the vibrations by twenty times. The spiral is a spiral channel whose membrane that covers the inner surface is formed by sensory cells filiform. When the sound wave reaches this part of the ear, it goes to stimulate, depending on the height of the sound, different cells. High sounds stimulate cells more rigid and thin placed at the mouth of the spiral while the quieter sounds stimulate cells more extensive and flexible placed at the center of the channel. From the stress of every cell is produced an electrical impulse that reaches the brain through the fibers of the auditory nerve. At this point, the brain decodes the sounds and interprets them. The neurons of the auditory nerve can be compared to a very small battery that is downloaded to each stimulus but can be recharged very fast thanks to its metabolism.
But because the ears are two?
The organism can not only pick up the sound but also to decipher the origin. In fact, the sound reaches the ear before the source of that sound because the nerve impulses to the brain in a different way. This difference, thanks to cerebral cortex, allows the brain to decipher the origin of the sound. Some loud sounds can prevent the perception of others of lesser intensity which however, could be important for the safety of the individual, especially when you are driving a vehicle. Every day the ears are subjected to so many sounds and noises such as road traffic, radio, television, supermarkets, etc.. Each sound helps to raise the minimum sound pressure level required to stimulate the neurons of the auditory nerve known as the hearing threshold, the raising of the hearing threshold reaches its peak in about two minutes of exposure to noise and decreases slowly thereafter.

All this not only affects the individual’s activities such as driving a vehicle or taking a flight but causes hearing damage. After a night at the club, the ears have a hearing threshold higher than normal. This can even cause temporary deafness and must be taken into account if you are put on the wheel of a vehicle.














